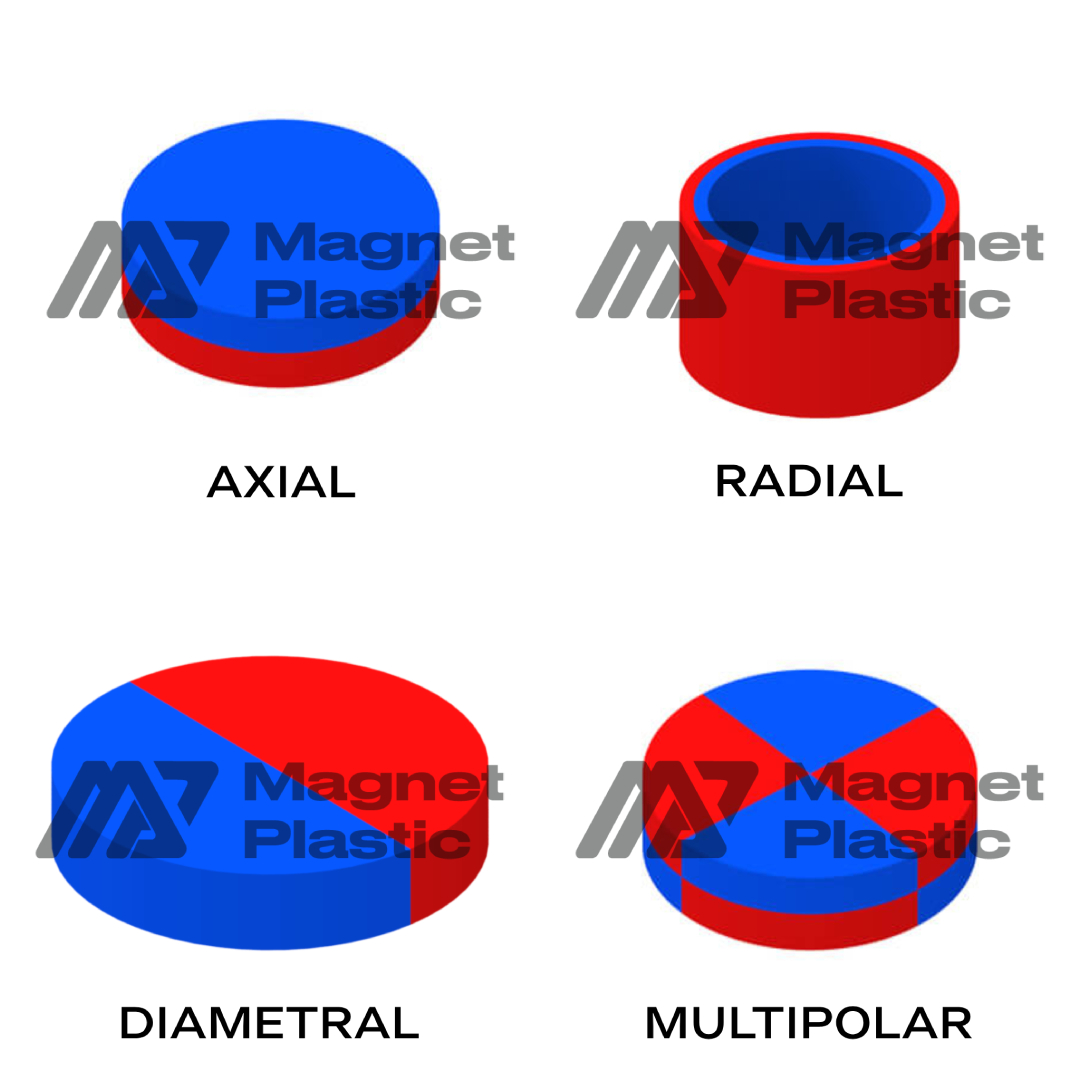
Deciphering Magnetization Directions in Magnets
The direction of magnetization in magnets is a fundamental aspect that determines their applications and properties. In this article, we will delve into various types of magnetization: axial, radial, diametral and multipolar, exploring their specific characteristics and uses.
- Axial Magnetization:
Axial magnetization implies that the magnetic poles are located along the main axis of the magnet. This in-line orientation is perfect for applications that require a magnetic force in a specific direction. Magnets with axial magnetization find use in electric motors, for example, elevators, and magnetic closure systems, taking advantage of their design to generate unidirectional magnetic fields.

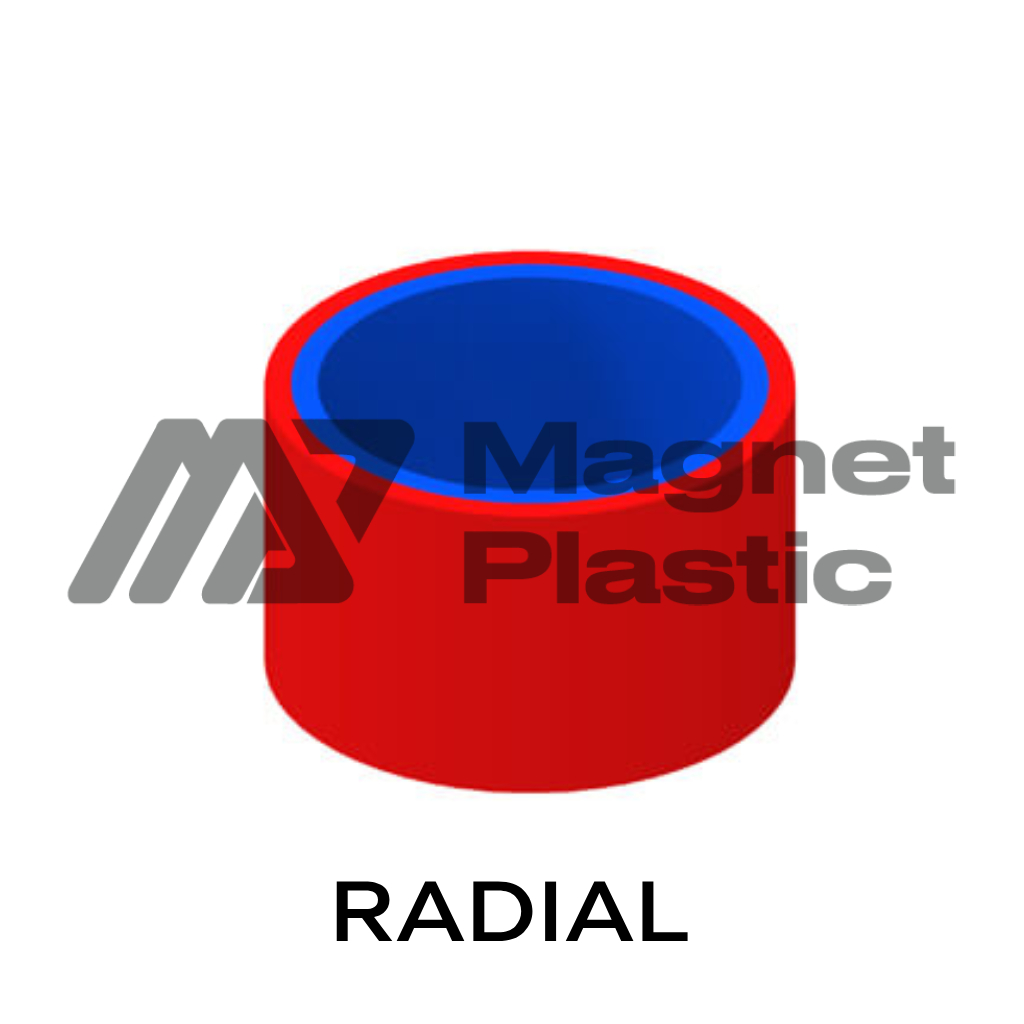
- Radial Magnetization:
In radial magnetization, the magnetic poles are arranged along the radius of the magnet. This configuration allows the magnetic force to flow from the center outwards. This direction of magnetization is especially beneficial in loudspeakers and hearing systems, where the radial distribution of the magnetic field improves overall performance.
- Diametral Magnetization:
Diametral magnetization implies that the magnetic poles are located along the diameter of the magnet. This arrangement generates a magnetic field that flows from one side of the magnet to the other. Magnets with diametral magnetization are ideal for applications that require precise magnetic fluxes, such as switches and toys.

- Multipolar Magnetization:
Multipolar magnetization involves the presence of multiple magnetic poles on the surface of the magnet. This complex arrangement creates a detailed and varied magnetic field. Magnets with multipolar magnetization are essential in applications that require specific and detailed magnetic fields, such as magnetic sensors, generators and medical devices.

Strategic Selection of Magnetization Types:
The choice of the type of magnetization depends directly on the application. Axial magnetization is ideal for linear magnetic forces, radial for equal distributions, diametral for precise magnetic fluxes and multipolar for complex magnetic fields. Understanding these options is vital when selecting magnets for specific purposes.
Conclusion: Exploring Diversity in Magnetization Management
In conclusion, the direction of magnetization plays an essential role in the properties and applications of magnets. The variety of types of magnetization, whether axial, radial, diametral or multipolar, opens a range of possibilities for various technological innovations. By understanding and strategically choosing the type of magnetization, you can maximize magnetic efficiency in various industries.
